This randomized, clinical trial evaluated 60 premature neonates with rds. Surfactant treatment improves oxygenation and reduces the need for ecmo without an increase in morbidity in neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome (loe 2).

Techniques Of Modified Insure In Spontaneously Breathing Preterm Download Table
Since surfactant replacement therapy has been introduced in 1980s, it has proven its effect in premature neonates with surfactant deficiency.
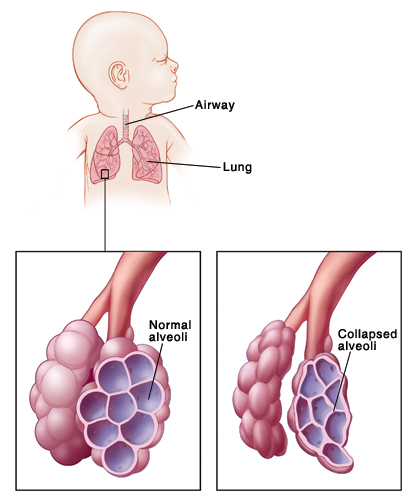
Surfactant in premature neonates. Some inherited surfactant gene defects have also been implicated. The incidence of rds correlates strongly with severity of prematurity. Despite its widespread use, the optimal method of surfactant administration in preterm infants has yet to be clearly determined.
Discoveries that led to its development as a therapeutic agent Abstract exogenous surfactant therapy has been part of the routine care of preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome (rds) since the beginning of the 1990s. The insufficient production of surfactants by preterm neonates leads to decreased lung compliance and increased alveolar surface tension, both of which increase the risk of alveolar collapse.
It is formed by type ii pneumocytes from about 20 weeks of gestation. Numbered envelopes randomly assigned 30 neonates to the intervention group to receive 2.5 ml/kg/dose surfactant (curosurf) via lma and 30 to the control group to receive 2.5 ml/kg/dose surfactant via an endotracheal tube using the insure technique, exclusively during the. Respiratory distress syndrome (rds) is the prototypical disease of surfactant deficiency in preterm newborn infants.
Mean gestational age was 29±2.8 weeks and mean birth weight was 1273±487gms. Premature neonates are at high risk of suffering respiratory distress syndrome (rds) soon after birth. Surfactant therapy for respiratory distress.
Surfactant treatment has become the standard of care in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome (rds). Discoveries that led to its development as a therapeutic agent span the whole of the 20th century but it was not until 1980 that the first suc. Early administration of exogenous surfactant via the endotracheal tube to premature infants significantly reduces the severity of rds.
Surfactant was used as single dose in 41(78%) neonates at 6.1±6.6hours of life or two doses in 11(22%). In general, defects in surfactant metabolism occur due to accelerated breakdown of the surfactant complex by oxidation, proteolytic degradation, and inhibition [43, 44]. The most likely mechanism explaining the requirement of additional exogenous surfactant in early onset infection is.
Defective surfactant metabolism leads to both morbidity and mortality in preterm and term neonates. Surfactant creates a continuously reforming surface layer Infants born at the extremes of viability (≤28 weeks gestational age) have immature lungs with severe deficiency of surfactant production.
Success of this procedure and. Most neonates with rds are premature, and their deficiency of endogenous surfactant is related to a relative lack of mature type ii pneumocytes. The syndrome occurs when microscopic sacs called alveoli in infant lungs do not produce.
Surfactant has revolutionized the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome and some other respiratory conditions that affect the fragile neonatal lung. Surfactant replacement has not been shown to affect the incidence of neurologic, developmental, behavioral, medical, or educational outcomes in preterm infants (loe 2). The surfactant is indicated in all neonates with rds.
Cpap has also successfully been used to manage small preterm neonates with rds, and when combined with surfactant therapy, reduced the need for ventilation in infants with moderately severe rds, especially when administered early or prophylactically.[252,253] unfortunately, these neonates still require intubation to administer the surfactant; Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, previously called hyaline membrane disease, is a respiratory disease affecting premature newborns.neonatal respiratory distress syndrome involves shallow breathing, pauses between breaths that last a few seconds, or apnea, and a bluish tinge to the infant’s skin. Term infants of mothers with poorly controlled diabetes may also present with rds, because fetal hyperinsulinism interferes with the glucocorticoid axis that governs surfactant biosynthesis ( , 21 ).
An increased requirement for surfactant therapy for early onset pneumonia has been previously reported in late preterm and term neonates , while a slower response to surfactant therapy was found in specific types of infection such as group b streptococcal pneumonia. Surfactant replacement is a standard and widely used therapy for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (rds) among premature neonates. The route of administration is intratracheal.
Exogenous surfactant therapy has been part of the routine care of preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome (rds) since the beginning of the 1990s. Since surfactant therapy is important in various respiratory conditions in premature neonates, this proposed study reviews the incidence, outcome & their clinical issues in surfactant replacement therapy. A total of 52 premature neonates received surfactant.
In the past, studies on outcomes of infants with respiratory distress have primarily focused on extremely premature infants, leading to a gap in knowledge and understanding of the developmental biology and mechanism of pulmonary diseases in lpt neonates. Only 16(31%) mothers had received antenatal dexamethasone. Surfactant in preterm infants introduction pulmonary surfactant is a complex mixture of phospholipids and proteins that serves to reduce alveolar surface tension.

Pdf Surfactant Replacement Therapy For Preterm And Term Neonates With Respiratory Distress

Prophylactic Low-dose Paracetamol Administration Associated With Lowered Rate Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus In Preterm Infants Impact On Outcome And Pain Perception - Pediatrics Neonatology

Pediatrics Notes Respiratory Distress Syndrome Of Newborns - A Brief Discussion Respiratory Distress Syndrome Respiratory Syndrome
Respiratory Distress Syndrome In The Premature Infant Saint Lukes Health System

Surfactant Administration In Preterm Infants Drug Development Opportunities - The Journal Of Pediatrics

Pdf Is There A Difference In Surfactant Treatment Of Respiratory Distress Syndrome In Premature Neonates A Review

Pdf The Role Of Surfactant Treatment In Preterm Infants And Term Newborns With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Semantic Scholar

Understanding Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rds Babyhealth Nicu Nurse Education Pediatric Nursing Neonatal Nurse
Pdf Estimation Of Early Life Endogenous Surfactant Pool And Cpap Failure In Preterm Neonates With Rds
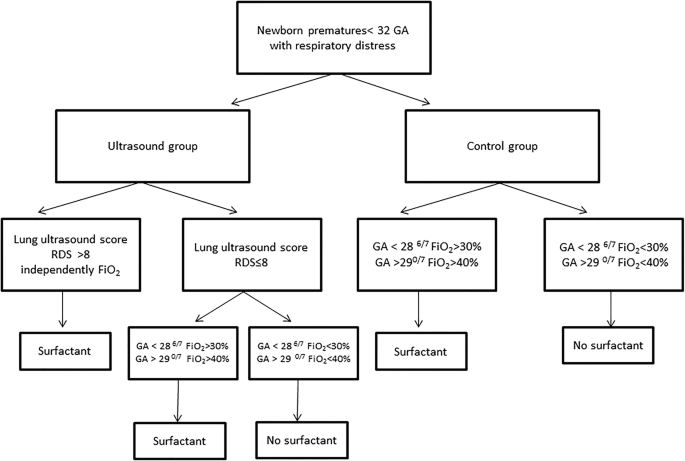
Early Surfactant Replacement Guided By Lung Ultrasound In Preterm Newborns With Rds The Ultrasurf Randomised Controlled Trial Springerlink

Pin By Prashanth Super Speciality On Did You Know Neonatal Intensive Care Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Neonatology

Lung Recruitment Before Surfactant Administration In Extremely Preterm Neonates With Respiratory Distress Syndrome In-rec-sur-e A Randomised Unblinded Controlled Trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
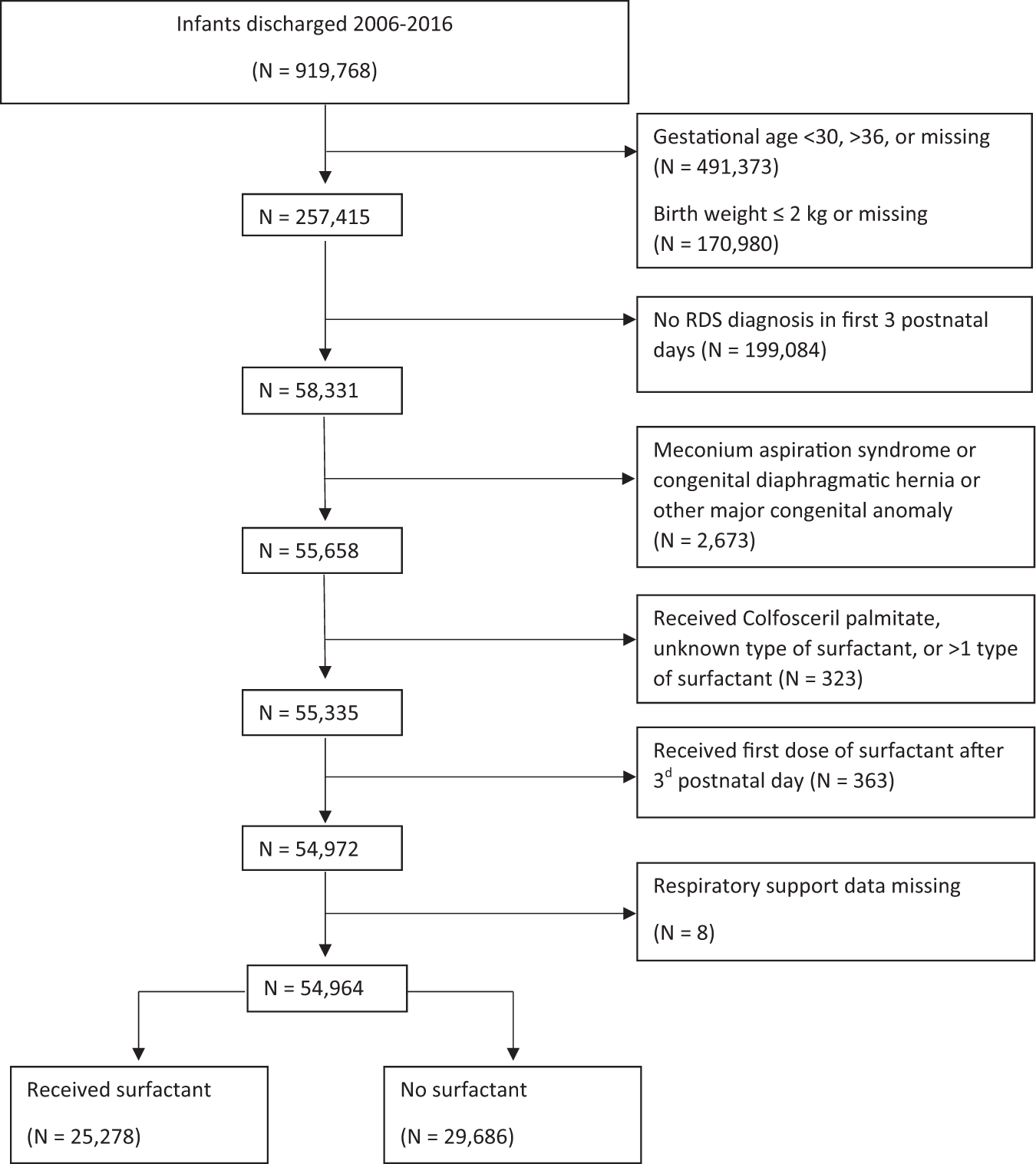
Outcomes Associated With Surfactant In More Mature And Larger Premature Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Journal Of Perinatology

Respiratory Distress Syndrome In Preterm Neonates In The Era Of Precision Medicine A Modern Critical Care-based Approach - Pediatrics Neonatology

Surfactant Replacement Therapy A Milestone In Neonatology Efcni

Pin On Nursing School

Pdf Radiological Assessment Of Post Surfactant Changes In Respiratory Distress Syndrome Semantic Scholar
Pdf Effects Of Surfactants On Preterm Infant Lungs

Pdf Surfactant Replacement Therapy For Preterm And Term Neonates With Respiratory Distress Semantic Scholar